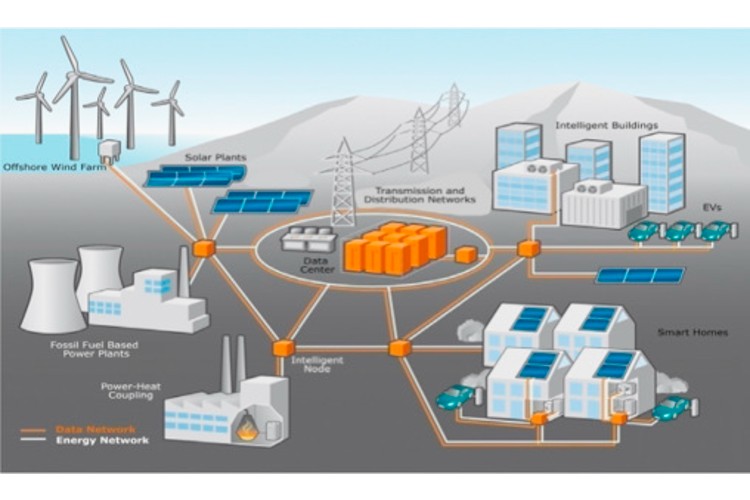
The global energy landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by growing environmental concerns, the push for decarbonization, and the rising demand for cleaner, more sustainable power sources. Central to this evolution is the integration of renewable energy sources with smart grid technologies, a market that is set to redefine how electricity is generated, distributed, and consumed. Between 2023 and 2031, this market is projected to grow at a remarkable pace, fueled by government incentives, technological advancements, and a paradigm shift toward decentralized power systems.
The Concept of Renewable Energy Integration with Smart Grids
At its core, renewable energy integration with smart grids involves the seamless connection of variable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass into an intelligent, responsive electrical grid. Smart grids use digital communication, automation, and real-time data analytics to manage electricity flows efficiently and ensure grid stability despite the intermittent nature of renewables.
This integration is crucial to achieving global climate goals and meeting the energy needs of the future, where supply and demand must be balanced dynamically, often in real time.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Integration with Smart Grids
Enhanced Grid Reliability and Efficiency
Smart grids enable better load management, reduce energy losses, and prevent blackouts by automatically detecting and responding to grid disturbances.
Optimized Use of Renewable Sources
Intelligent grid systems improve forecasting, scheduling, and utilization of renewable resources, maximizing their contribution to the energy mix.
Cost Savings for Utilities and Consumers
By reducing operational costs and enabling demand-side management, smart grids lead to long-term economic benefits across the energy ecosystem.
Empowered Consumers
With advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), consumers can monitor and control their energy usage, participate in demand response programs, and even feed power back into the grid via distributed energy resources (DERs).
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Integration supports the global transition away from fossil fuels, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions and a healthier environment.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its vast potential, the integration of renewable energy with smart grids faces several challenges:
Intermittency of Renewable Sources
Solar and wind power depend on weather conditions, making grid balancing complex without sufficient energy storage solutions.
Infrastructure Modernization Costs
Upgrading existing power infrastructure to smart grid standards involves substantial capital investments and long-term planning.
Cybersecurity Risks
As smart grids become more interconnected and reliant on data, they become vulnerable to cyberattacks that could disrupt power supply or compromise consumer privacy.
Regulatory and Policy Barriers
Differing energy regulations across countries or regions can hinder the uniform implementation of smart grid technologies.
Future Outlook and Opportunities (2023–2031)
The market for renewable energy-smart grid integration is poised for robust growth over the forecast period. According to recent estimates, the market is expected to witness a CAGR exceeding 15% from 2023 to 2031, driven by:
Expansion of Utility-Scale Renewable Projects
Countries across Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America are investing heavily in solar farms and wind parks.
Smart City Initiatives
Urban centers are turning to smart grids to manage electricity more efficiently and reduce environmental impact.
Growth of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EVs create both new challenges and opportunities for grid management, especially when paired with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies.
Advancements in AI, IoT, and Blockchain
These technologies will play a vital role in predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and decentralized energy trading.
Supportive Government Policies
Incentives, grants, and decarbonization targets are encouraging utilities and grid operators to adopt integrated smart grid solutions.
Conclusion
The integration of renewable energy sources with smart grids represents a cornerstone of the global transition to a sustainable, low-carbon energy future. While challenges remain, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, particularly as technology continues to evolve and mature. Between 2023 and 2031, this market will be a key enabler of energy resilience, efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
As stakeholders across the energy spectrum—from policymakers and utility companies to tech innovators and consumers—embrace this integration, the world moves one step closer to achieving energy independence and climate goals. The road ahead is not just smart—it’s sustainable, inclusive, and transformative.