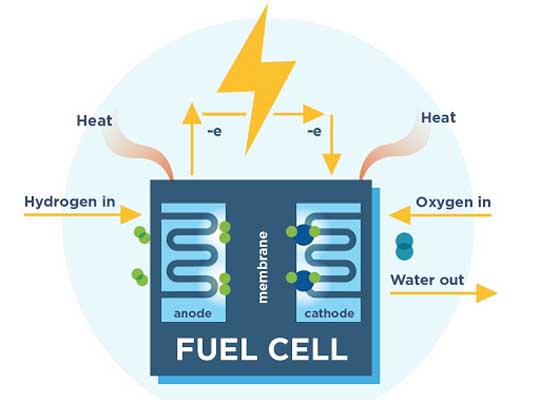
A Hydrogen fuel cell is a device that generates electrical power by a chemical reaction via conversion of fuel (hydrogen) into electricity. Although batteries and fuel cells are both considered electrochemical cells and consist of similar structures, fuel cells require a continuous source of oxygen and fuel to run, similar to how an internal combustion engine needs a constant flow of gasoline or diesel.
Growth in demand for electric vehicles is driving the market for hydrogen fuel cells. An increase in carbon emissions has attracted the government’s attention to the usage of electric vehicles. Another factor impacting the market is the growing concern for the environment. The over-exploitation of fossil fuels has created ecological concerns due to harmful gas emissions. The need for reduced dependence on oil and diesel are propelling the demand of the market.
The global Hydrogen Fuel Cell market was valued at USD 10.49 Billion in 2018 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.4% from 2019 to reach USD 49.52 Billion by the year 2026. Hydrogen fuel cells are known to be used in a broad range of applications like cars, buildings, electronic devices, trucks, and/or backup power systems. As those fuel cells can be grid-independent, they are an attractive option for critical load functions such as telecommunication towers, data centers, emergency response systems, hospitals, and even military applications for national defense.
Read more @ https://www.reportsanddata.com/report-detail/hydrogen-fuel-cell-market
A Hydrogen fuel cell is a device that generates electrical power by a chemical reaction via conversion of fuel (hydrogen) into electricity. Although fuel cells are considered to be electrochemical cells and consist of similar structures, fuel cells require an uninterrupted source of oxygen and fuel to run, similar to how an internal combustion engine that needs a constant flow of gasoline or diesel.
Manufacturers are zeroing-in on the hydrogen economy as the concern for the environment is growing. Hydrogen fuel cells are also scalable. They can be combined to form stacks, which in turn can be combined to form larger systems. These fuel systems vary in sizes and power, from portable systems for smartphone battery recharging, to combustion engine replacements for electric vehicles, to large-scale, multi-megawatt installations providing electricity directly to the utility grid.
Important factors:
- Fuel cells do not run down or face the need to recharge, as compared to the batteries. These also reduce carbon dioxide emission by half only if the hydrogen is produced by natural gas. The emission gets reduced by 90% if hydrogen is produced by renewable sources such as wind and solar.
- Hydrogen fuel cells have a driving range of more than 300 miles on one tank of hydrogen fuel. As they have no moving parts, they require no change of oil.
- Fuel cells are twice as efficient as an internal combustion engine, and a car running on them travels farther on that tank of hydrogen than a traditional car would on gasoline.
- Government initiatives have led to 30 public retail hydrogen fueling stations in California, with plans to install another 100 more. These efforts are encouraging the consumption of hydrogen-fueled cars with the access of hydrogen wherever they go within the region.
- Hydrogen-fuelled cars are limited as people do not buy these cars if hydrogen refueling stations are not easily accessed, and companies will not build them if they do not have consumers with hydrogen-fuelled vehicles.
Growth in demand for electric vehicles is driving the market for hydrogen fuel cells. An increase in carbon emissions has attracted the government’s attention to the usage of electric vehicles. Another factor impacting the market is the growing concern for the environment. The over-exploitation of fossil fuels has created ecological concerns due to harmful gas emissions. The need for reduced dependence on oil and diesel are propelling the demand of the market.
Europe is taking giant steps towards the adoption of hydrogen fuel cells. The world’s first hydrogen-powered trains are currently operational in northern Germany on a 100km stretch of track. Even though it is costlier than the existing diesel locomotives, the new zero-emissions engines are kinder to the environment. Key players in the Hydrogen Fuel Cell market are Toshiba Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Hyster-Yale Materials Handling, Inc., Fuel cell Energy, Intelligent Energy, SFC Energy AG, Ballard Power, Plug Power Inc., Bloom Energy and Hydrogenic Corporation, among others. The companies have adopted various strategies, which include mergers & acquisitions, and partnerships to hold ongoing trails and come up with new developments in the market.
Further key findings from the report suggest
- Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells uses precious metals like platinum, along with a polymer for the catalyst. It is known to be preferable over other technologies so that it can be operated at cooler temperatures that are between 80 to 200 degrees Fahrenheit. It operates between 40%-60% efficiency, which can also handle large and sudden shifts in power output; also, they are used in telecommunications, residential markets, and data centers.
- The air-cooled type has dominated the segment of hydrogen fuel cell product type attaining a CAGR of 26.5%. Passing of ambient air either through the additional cooling plates or cathode is the simplest method of removing waste heat from fuel cells. Examples like the Suzuki Burgmann fuel cell scooter which utilizes a 1.6 kW air-cooled stack, and the Microcap H2EV which utilizes a 3.0 kW Horizon open cathode fuel cell in a battery hybrid arrangement.
- Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles also combine the refueling and range of conventional cars and the recreational benefits of driving on electricity. Refueling a fuel cell vehicle is compared to refuel a car or a truck. Pressurized hydrogen is available at hydrogen refueling stations, and takes less than 10 minutes to fill current models.
- The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a hub for the adoption of hydrogen power cell technology with the highest CAGR of 24.6%. The region counts many countries as pioneers, like Japan, South Korea, and more recently, China.
- The recent impetus on the adoption of clean energy sources, and China clamping down on its coal usage for energy generation has opened a huge market for hydrogen fuel cells in the region.
- Other countries, especially India, are at a nascent stage of development and are expected to be future growth drivers. The North American region also shows significant promise, as Canada and the U.S move towards investment in green energy. California has the largest infrastructure base on the continent and is responsible for significant innovation in technology.
Key participants include Toshiba Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Materials Handling Inc., Fuel cell Energy Inc., Intelligent Energy Limited, SFC Energy AG, Ballard Energy Corporation, Plug Power Inc., Bloom Energy Corporation, Hydrogenic Corporation
For the purpose of this particular report, Reports and Data segments the Hydrogen Fuel Cell market on the basis of: product type, technology, application, and regions
Product Type (Revenue, USD Million; Volume in Megawatt, 2017–2027)
- Liquid-Cooled Type
- Air-Cooled Type
Technology Type (Revenue, USD Million; Volume in Megawatt, 2017–2027)
- Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC)
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells (PAFC)
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)
- Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFC)
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC)
Application (Revenue, USD Million; Volume in Megawatt, 2017–2027)
- Automotive
- Stationary
- Material Handling Equipment
- Electricity
- Portable Power
Download Free Sample copy of Report @ https://www.reportsanddata.com/sample-enquiry-form/2061